Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are small, membrane enclosed organelles that contain enzymes involved in a variety of metabolic reactions. Peroxisomes contain a variety of enzymes, which primarily function together to rid the cell of toxic substances, and in particular, hydrogen peroxide. Although peroxisomes are structurally similar to lysosomes, they are assembled like mitochondria and chloroplasts, from proteins that are synthesized on free ribosomes and then imported into peroxisomes as completed polypeptide chains. Like mitochondria and chloroplasts, however, peroxisomes are thought to acquire their proteins by selective import from the cytosol, but because they have no genome, all of their proteins must be imported. Peroxisomes are found in all eukaryotic cells. They contain oxidative enzymes such as catalase and urate oxidase. A variety of substrates are broken down by oxidative reactions in peroxisomes including uric acid, amino acids, and fatty acids. Peroxisomes are diverse organelles and even in the various cell types of a single organism they may contain different sets of enzymes.
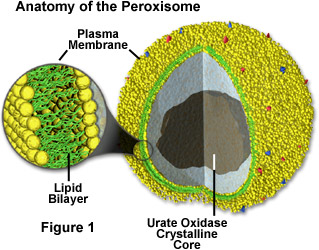
https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/peroxisomes/peroxisomes.html
Comments
Post a Comment